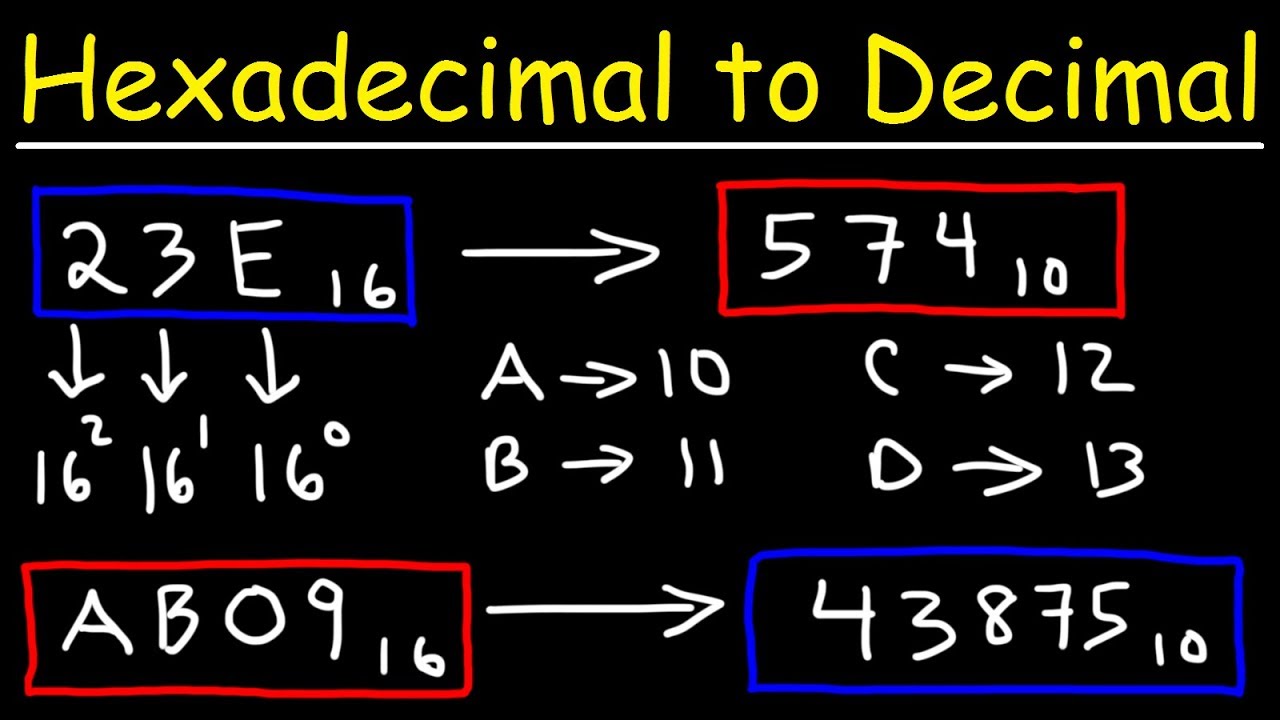
Hexadecimal to Decimal Number systems form the backbone of mathematics, computing, and digital technology. Every calculation performed by a computer, smartphone, or electronic device relies on specific number systems to represent and process data efficiently. Among these, the decimal and hexadecimal number systems are two of the most widely used. Understanding how hexadecimal to decimal conversion works is an essential skill for students, programmers, and anyone interested in computer science or digital logic.
The decimal number system is the most familiar to humans because it is based on ten digits, from 0 to 9. We use it in everyday life for counting, measuring, financial transactions, and calculations. On the other hand, the hexadecimal number system is primarily used in computing and electronics. It is a base-16 system that uses digits from 0 to 9 and letters from A to F to represent values. While hexadecimal may seem complex at first, it is designed to simplify how computers represent large binary numbers.
Hexadecimal to decimal conversion is the process of translating a number written in base-16 into its equivalent base-10 value. This conversion is important because while computers and programmers often work with hexadecimal for efficiency, humans usually interpret and analyze values in decimal form. Learning this conversion bridges the gap between machine-level data and human understanding.
In this article, we will explore hexadecimal and decimal number systems in detail, explain the conversion process step by step, discuss formulas, tools, and real-world applications, and provide examples to help you master hexadecimal to decimal conversion with confidence.
Understanding the Hexadecimal Number System
The hexadecimal number system is a base-16 numbering system, meaning it has sixteen unique symbols to represent values. These symbols include the digits 0 through 9 and the letters A, B, C, D, E, and F. Each letter represents a decimal value: A equals 10, B equals 11, C equals 12, D equals 13, E equals 14, and F equals 15. This expanded set of symbols allows hexadecimal to represent large values more compactly than binary or decimal.
One of the key features of the hexadecimal system is its positional value structure. Just like decimal numbers, hexadecimal numbers use place values, but instead of powers of 10, they use powers of 16. For example, the rightmost digit represents 16⁰, the next represents 16¹, followed by 16², and so on. Each digit’s value is determined by multiplying it with its corresponding power of 16. This structure makes hexadecimal numbers easy to convert into other systems when the rules are understood.
Hexadecimal is widely used in computing because it provides a convenient shorthand for binary values. Since one hexadecimal digit represents exactly four binary bits, long binary sequences can be grouped and expressed in a much shorter hexadecimal format. This makes reading, writing, and debugging machine-level data significantly easier for programmers and engineers.
In real-world technology, hexadecimal numbers appear in memory addresses, machine instructions, error codes, and even web design. For example, color codes in HTML and CSS use hexadecimal values to define colors precisely. Understanding the hexadecimal system is the first step toward mastering hexadecimal to decimal conversion.
Understanding the Decimal Number System
The decimal number system is a base-10 system and is the most commonly used number system by humans. It consists of ten digits: 0 through 9. Each digit’s position in a decimal number represents a power of 10. For example, in the number 345, the digit 3 represents 3 × 10², the digit 4 represents 4 × 10¹, and the digit 5 represents 5 × 10⁰. This positional value system makes decimal numbers intuitive and easy to understand.
Because humans have ten fingers, the decimal system evolved naturally as a counting method. It is used universally in education, commerce, science, and everyday communication. When we talk about quantities, prices, distances, or statistics, we almost always use decimal representation. This widespread use makes decimal the preferred system for interpretation and analysis.
In computing, decimal numbers are often used when displaying information to users, even though internal processing may rely on binary or hexadecimal. For example, memory usage, file sizes, and performance metrics are typically shown in decimal or decimal-based formats to make them understandable to non-technical users.
When converting hexadecimal to decimal, the goal is to translate machine-friendly values into a human-friendly format. By understanding how decimal place values work, it becomes easier to grasp how hexadecimal digits translate into equivalent decimal values. This understanding forms the foundation for accurate and reliable hexadecimal to decimal conversion.
Hexadecimal to Decimal Conversion Method
The hexadecimal to decimal conversion method is based on expanding the hexadecimal number using place values and powers of 16. Each digit in the hexadecimal number is multiplied by 16 raised to the power of its position, starting from zero on the right. The results are then added together to obtain the final decimal value. While this may sound complex, it becomes straightforward with practice.
To begin the conversion, write down the hexadecimal number and identify the position of each digit. The rightmost digit is multiplied by 16⁰, the next digit by 16¹, then 16², and so on. Next, replace any hexadecimal letters with their decimal equivalents. For example, A becomes 10 and F becomes 15. This step ensures all values are in decimal form before calculation.
After multiplying each digit by its corresponding power of 16, add all the results together. The sum is the decimal equivalent of the hexadecimal number. This method works for both small and large hexadecimal values and does not require any special tools, making it ideal for exams and foundational learning.
Common mistakes during hexadecimal to decimal conversion include forgetting to convert letters into decimal values or using powers of 10 instead of powers of 16. Paying close attention to place values and practicing with examples can help avoid these errors. Once mastered, this method becomes a reliable way to perform conversions manually.
Hexadecimal to Decimal Conversion Formula
The hexadecimal to decimal conversion formula provides a structured mathematical approach to the conversion process. The general formula is based on summing each digit multiplied by 16 raised to the power of its position. It can be written as:
Decimal Value = Σ (digit × 16ⁿ), where n represents the position index starting from zero on the right.
This formula is especially useful when dealing with longer hexadecimal numbers or when explaining the conversion process in academic or technical contexts. By applying the formula systematically, you can ensure accuracy and consistency in your calculations. It also helps in understanding how each digit contributes to the final decimal value.
Using the formula reinforces the concept of positional value and powers of 16. It highlights why hexadecimal numbers grow rapidly in value and why they are efficient for representing large binary data. This mathematical clarity is particularly helpful for students studying computer science, electronics, or digital systems.
Practicing the formula with different examples improves speed and confidence. Over time, the formula becomes second nature, allowing you to convert hexadecimal to decimal values quickly, whether on paper, in exams, or during programming tasks.
Using Hexadecimal to Decimal Conversion Tools
While manual conversion is important for learning, hexadecimal to decimal conversion tools offer speed and convenience. Online calculators and software utilities can instantly convert hexadecimal values into decimal form, saving time in practical applications. These tools are widely used by programmers, network engineers, and students.
The main advantage of using conversion tools is accuracy, especially when dealing with very large hexadecimal numbers. They reduce the risk of human error and are ideal for real-world scenarios where efficiency matters. Many tools also support batch conversions and additional number systems, making them versatile and user-friendly.
However, relying solely on tools without understanding the underlying process can be limiting. Manual knowledge helps in debugging, verifying results, and performing conversions when tools are unavailable. A balanced approach—understanding the method while using tools for efficiency—is the best strategy.
When choosing an online converter, it is important to use reliable and reputable sources. Some tools also provide step-by-step explanations, which can be helpful for learning and revision. These resources complement manual practice and enhance overall understanding.
Hexadecimal to Decimal Conversion in Computer Science
Hexadecimal to decimal conversion plays a significant role in computer science and information technology. Programmers often encounter hexadecimal values when working with memory addresses, machine code, and system-level programming. Converting these values into decimal helps in analysis, debugging, and documentation.
One common example is color representation in web development. Hexadecimal color codes define RGB values, which are internally processed as numbers. Understanding how these hexadecimal values translate into decimal helps developers fine-tune colors and troubleshoot design issues. Similarly, network protocols and hardware registers often use hexadecimal notation.
In cybersecurity and digital forensics, hexadecimal to decimal conversion is used to interpret data packets, logs, and encoded information. Accurate conversion ensures correct analysis and decision-making. This highlights the importance of mastering conversion skills beyond academic use.
Overall, hexadecimal to decimal conversion is a foundational skill that supports deeper understanding of how computers work. It connects abstract numerical representation with practical application, making it invaluable in technical fields.
Conclusion
Hexadecimal to decimal conversion is an essential concept in mathematics and computing. It allows us to translate machine-friendly hexadecimal values into human-readable decimal form. By understanding the structure of both number systems, learning the conversion method and formula, and practicing with examples, anyone can master this skill.
Whether you are a student, programmer, or technology enthusiast, knowing how to convert hexadecimal to decimal enhances your problem-solving abilities and technical literacy. With consistent practice and the right approach, hexadecimal to decimal conversion becomes simple, logical, and highly useful.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is hexadecimal to decimal conversion?
It is the process of converting a base-16 number into its base-10 equivalent.
Why is hexadecimal used instead of decimal in computing?
Hexadecimal efficiently represents binary data in a compact and readable format.
How do letters A–F convert into decimal numbers?
A = 10, B = 11, C = 12, D = 13, E = 14, F = 15.
Is hexadecimal to decimal conversion difficult to learn?
No, with practice and understanding of place values, it becomes easy.
Can I convert hexadecimal to decimal without a calculator?
Yes, using the manual method and formula, you can convert values by hand.
Where is hexadecimal to decimal conversion used in real life?
It is used in programming, web design, networking, electronics, and system analysis.
Also Read: Saf Instant Yeast